Java 9 new features

In this blog article, we follow the new features of Java 9, released on 21 September 2017. This Java version has a long story on how the voting committee discussed and changed their minds. As this release is quite large, I will concentrate on technical aspects only.
Java 9 syntax sugar
Try With Resource Enhancement
Java 7 introduced try-with-resources syntax.
try (BufferedReader reader1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file1.txt"));
BufferedReader reader2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file2.txt"))) {
// usage of readers
}
From Java 9 we can put resource declared outside the try-with-resource.
BufferedReader reader1 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file1.txt"));
BufferedReader reader2 = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("file2.txt"));
try (reader1; reader2) {
// usage of readers
}
Diamond Operator Extension
The diamond operator can now be used in internal anonymous classes:
UnaryOperator<Integer> increment = new UnaryOperator<>() {
@Override
public Integer apply(Integer integer) {
return integer + 1;
}
};
System.out.println(increment.apply(1));
Interface Private Method
From Java 9, interfaces can have private methods. This way, you can split logic to use smaller helper methods and use step down rule.
interface Doable{
default void doSomething() {
saySomething();
// some logic
}
private void saySomething() {
System.out.println("Hello world!");
}
}
Factories for immutable collections
Collections gain factory methods to produce immutable collections:
– List.of(),
– Set.of(),
– Map.of()
Example of usage:
List<Integer> list = List.of(1);
Set<Integer> set = Set.of(1);
Map<Integer, Integer> map = Map.of(1, 1);
List
Optional
or() method
Java 9 introduces the or() method which returns another Optional lazily if our Optional is empty.
If our first Optional has a defined value, the lambda passed to the or() method will not be invoked, and value will not be calculated and returned.
Optional<String> optional1 = Optional.of("text1");
Optional<String> optional2 = Optional.of("text2");
Optional<String> result = optional1.or(() -> optional2);
ifPresentOrElse() method
A new method ifPresentOrElse() was added Optional. You can execute action when the value is inside and when it is empty. (example contains not-simplified syntax):
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("text");
optional.ifPresentOrElse(
t -> System.out.println(t),
() -> {
System.out.println("empty");
});
The stream() Method
Optional got a new method stream() that allows us to treat the Optional instance as a Stream.
Optional<String> optional = Optional.of("text");
List<String> list = optional.stream()
.map(String::toUpperCase)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
Enhanced @Deprecated annotation
In Java 8 end earlier versions, @Deprecated annotation is just a Marker interface without property.
In Java 9, it is enhanced by two methods: forRemoval(boolean) and since(String) to serve this information.
Multi-Resolution Image API
In Java 9 it introduced a new Multi-Resolution Image API. MultiResolutionImage encapsulates a set of images with different heights and widths (that is different resolutions) and allows us to query them with our requirements.
Process API Improvements
They have added couple of new classes and methods to ease the controlling and managing of OS processes. Two new interfaces in Process API:
java.lang.ProcessHandlejava.lang.ProcessHandle.Info
JEP 266: More Concurrency Updates
In Java SE 9, CompletableFuture API was improved, to solve some problems raised in Java 8. They added support for delays and timeouts, some utility methods and better sub-classing. Let’s see some examples:
defaultExecutor()
Returns the default Executor used for async methods that do not specify an Executor (at least, one independent thread).
new CompletableFuture().defaultExecutor()
completeAsync()
CompletableFuture<T> completeAsync(Supplier<? extends T> supplier, Executor executor)
CompletableFuture<T> completeAsync(Supplier<? extends T> supplier)
The difference between these two overloaded methods is the existence of the second argument, where the Executor running the task can be specified. If none is provided, the default executor (returned by the defaultExecutor method) will be used.
delay
Execution of CompletableFuture with delay:
CompletableFuture<Object> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
future.completeAsync(() -> input, CompletableFuture.delayedExecutor(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS));
Publish-Subscribe Framework
Java 9 supports the Reactive Streams initiative by providing a publish-subscribe framework (also known as the Flow API). Reactive Streams is a standard for asynchronous stream processing with non-blocking back pressure. This specification is defined in the Reactive Manifesto, and there are various implementations of it, for example, RxJava or Akka-Streams.
Flow is a repository for four nested static interfaces whose methods establish flow-controlled components in which publishers produce data items that are consumed by one or more subscribers:
Publisher- A producer of data items that are received by subscribers,Subscriber- A receiver of data items,Subscription- Linkage between a Publisher and a Subscriber,Processor- A combination of Publisher and Subscriber for specifying a data-transformation function.
Jigsaw Project
Below are the various JEPs(JDK Enhancement Proposal) to be a part of the Jigsaw project:
- JEP 200: The Modular JDK – Use the Java Platform Module System, specified by JSR 376 and implemented by JEP 261, to modularize the JDK.
- JEP 201: Modular Source Code - Reorganize the JDK source code into modules, enhance the build system to compile modules, and enforce module boundaries at build time.
- JEP 220: Modular Run-Time Images - Restructure the JDK and JRE run-time images to accommodate modules and to improve performance, security, and maintainability
- JEP 260: Encapsulate Most Internal APIs - Encapsulate most of the JDK’s internal APIs by default so that they are inaccessible at compile time, and prepare for a future release in which they will be inaccessible at run time.
- JEP 261: Module System - Implement the Java Platform Module System, as specified by JSR 376, together with related JDK-specific changes and enhancements.
- JEP 282: jlink: The Java Linker - Create a tool that can assemble and optimize a set of modules and their dependencies into a custom run-time image as defined in JEP 220
Project Jigsaw is a modularization of the JDK and introduction of a module system for Java bringing about stronger encapsulation, smaller package footprint and reliable configuration to Java applications.
Example of module for Commons-lang3:
module commons.lang3 {
exports org.apache.commons.lang3;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.builder;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.concurrent;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.event;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.exception;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.math;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.mutable;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.reflect;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.text;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.text.translate;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.time;
exports org.apache.commons.lang3.tuple;
}
Keywords:
module- the module definition file starts with this keyword followed by its name and definition,requires- indicates that this module depends on another module,requires transitive <module name>- this means that any module that reads your module implicitly, also reads the transitive module,exports- indicates which public types of the module’s package are accessible to other modules,opens- indicates which public types of the module’s package are accessible to other modules onlyruntimevia Reflection APIs,uses <class/interface name>- indicates which service class/interface that this module is usingprovides <interface> with <implementation>- indicates that it providesimplementationforinterface
The java.base module contains commonly used JDK APIs like Utils, Collections, IO, Concurrency among others.
The dependency graph of the JDK modules is:
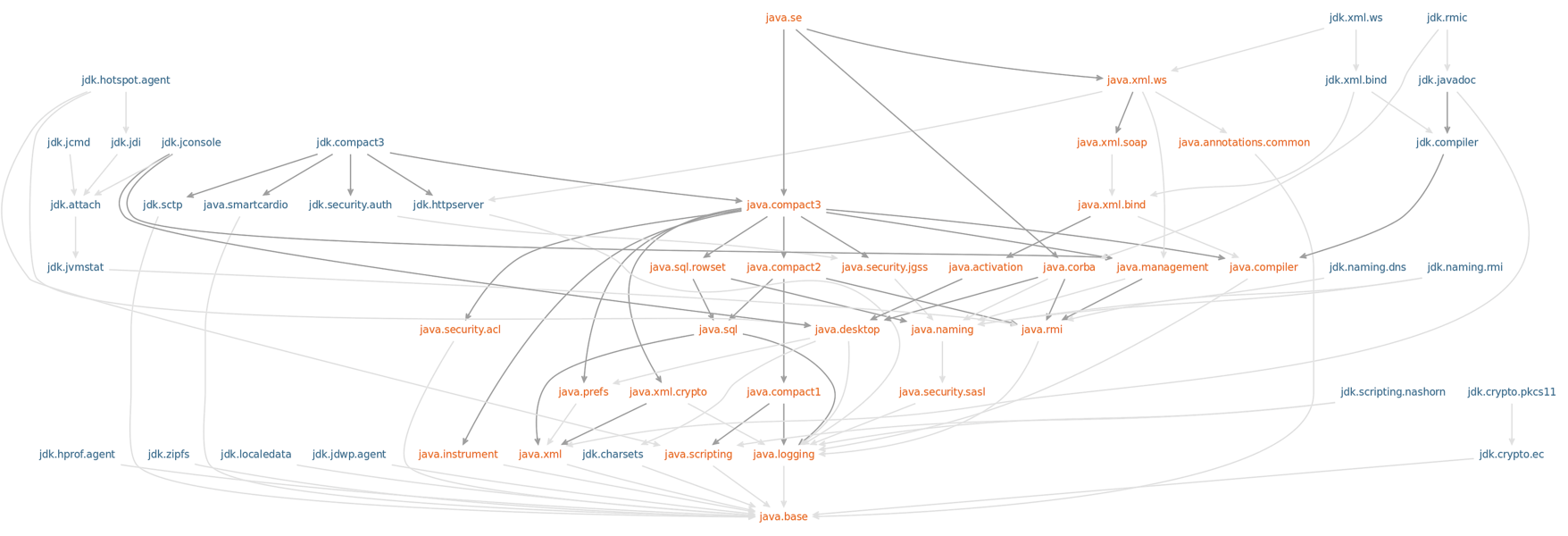
Tools for Modularity
jdeps– analyzes the code base to identify the dependencies on JDK APIs and the third party JARs,jdeprscan– analyzes the code base for usage of any deprecated APIs,jlink– creates a smaller runtime by combining the applications and the JDK’s modulesjmod– helps in working with jmod files. jmod is a new format for packaging the modules. This format allows including native code, configuration files, and other data that do not fit into JAR files.
JEP 222: jshell: The Java Shell (Read-Eval-Print Loop)
Provide an interactive tool to evaluate declarations, statements, and expressions of the Java programming language, together with an API so that other applications can leverage this functionality.
Example of usage:
$ jshell
jshell> int i = 2;
i ==> 2
jshell> System.out.println("Hello World " + i);
Hello World 2
Unified JVM Logging
This feature introduces a common logging system for all components of the JVM. It provides the infrastructure to do the logging.
java -Xlog -version
...
[0.019s][info][class,load ] java.lang.Object source: shared objects file
...
[0.026s][info][class,init ] 61 Initializing 'jdk/internal/misc/Unsafe' (0x0000000800095898)
...
Summary
Java 9 release was a big event. It introduced many big and small changes. For sure Jigsaw project became the most recognizable.